Atopic Dermatitis can be a challenging condition. Understanding symptoms and treatment options is critical for effective management and improving quality of life.
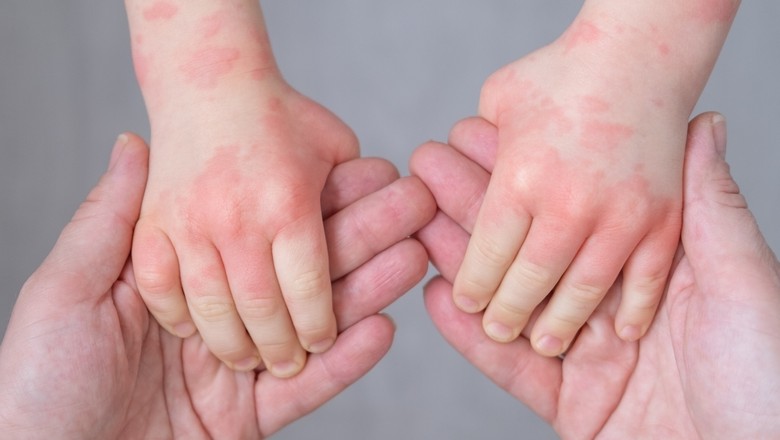
Atopic Dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often starts in childhood but can persist into adulthood. It is characterized by itchy, red, and swollen skin. This condition can have a significant impact on an individual's well-being, making daily activities uncomfortable due to persistent itching and visible skin changes.
Identifying the symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis is crucial for timely intervention and management. Common symptoms include:
Understanding what can trigger or worsen Atopic Dermatitis symptoms can help in managing the condition:
Managing Atopic Dermatitis involves a combination of treatments aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing flare-ups:
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home remedies can play a significant role in managing Atopic Dermatitis:
Seek medical advice if you notice:
Managing Atopic Dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes recognizing symptoms, avoiding triggers, and following an effective treatment regimen. By maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using prescribed treatments, and incorporating lifestyle adjustments, individuals with Atopic Dermatitis can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans.
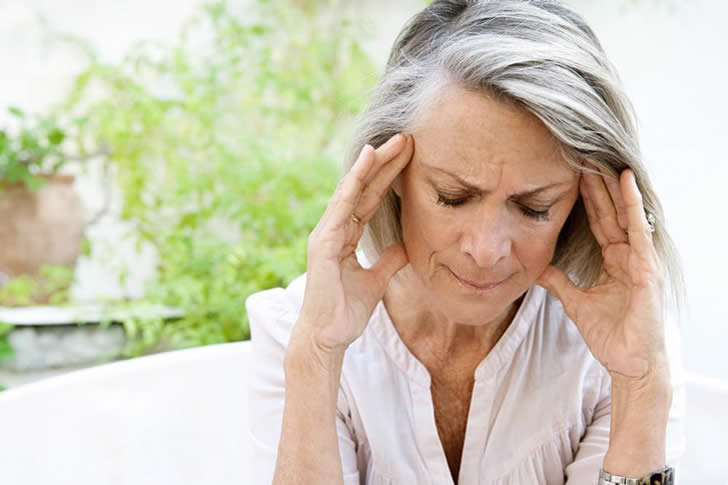

Dealing with migraines involves understanding symptoms and exploring effective treatments. This guide provides practical advice and tips to help manage your migraines better.
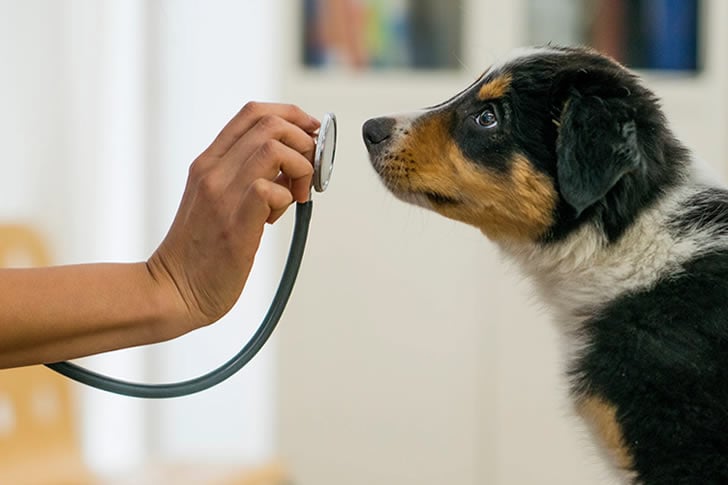

Ensuring your pet's well-being doesn't have to be expensive. Here are strategies for finding affordable veterinary clinics, practicing preventive care, and securing financial assistance.
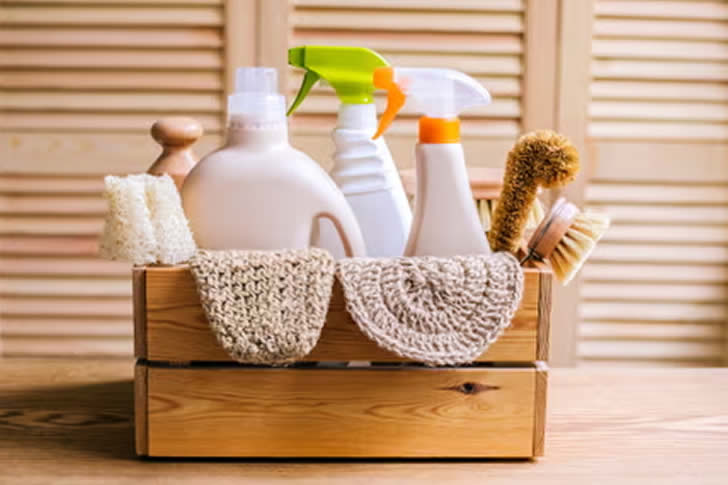

Keeping your home clean doesn't have to harm your health or the planet. Here’s how to use natural cleaning products for healthier, eco-friendly living.

Understanding and addressing mental health is vital. Recognizing signs and offering support can make a significant difference in someone’s life. Here are practical tips and advice to help you.
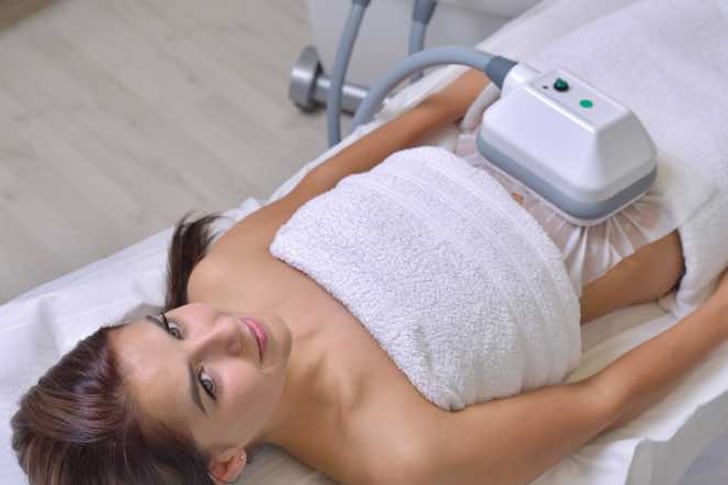
As we age, managing belly fat becomes crucial for overall health. This guide explores options for belly fat removal and how Medicare might support your health needs.

Incorporating a home sauna into your daily routine can offer numerous health and wellness benefits. This guide will provide practical advice on how to maximize those benefits effectively.

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) affects many individuals globally. This article explores the symptoms and treatment options available to support those suffering from PTSD.

Achieving your weight loss goals can be challenging. This guide provides essential advice on utilizing weight loss injections under the guidance of a healthcare provider.